Linux 系统的 SPI 设备编程
目录
SPI 通信协议 #
SPI 的全称是 Serial Peripheral Interface,是一个带时钟同步的全双工串行链接,使用主/从结构,用于连接微控制器和传感器、存储器和外设。常见的连接结构如下:
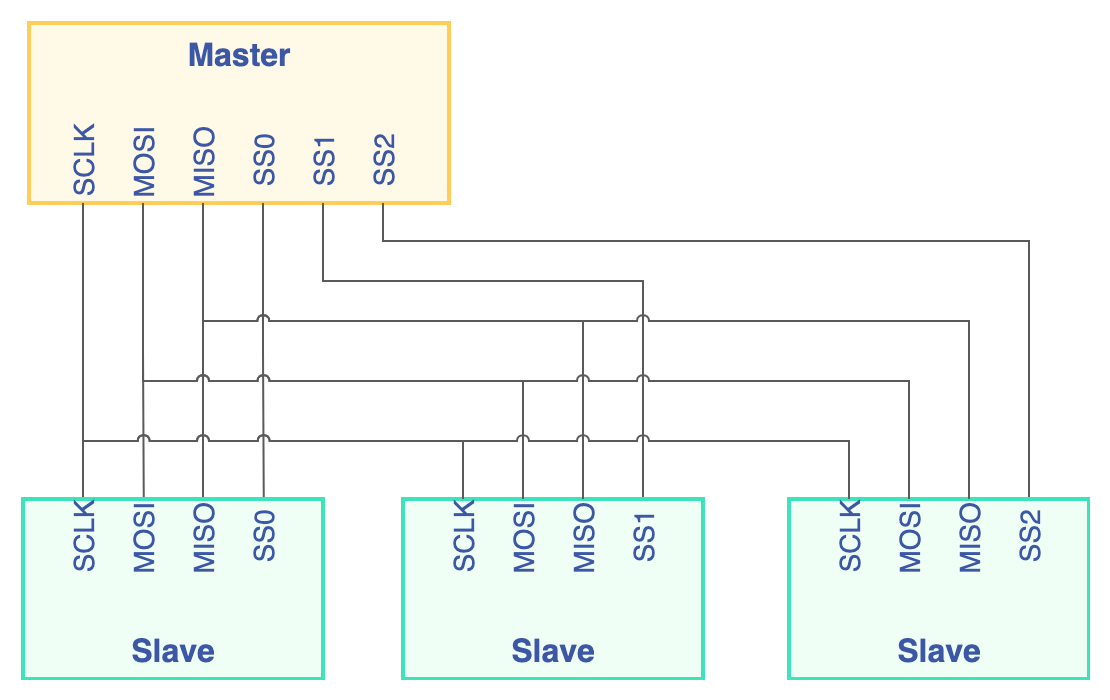
通信时需要四个信号:
- SCLK,Serial Clock,时钟信号,SPI 的时钟频率通常可以达到 10MHz,实际情况还依赖从机能够支持的时钟频率。
- MISO,Master In Slave Out,从机向主机发出的数据。
- MOSI,Master Out Slave In,主机向从机发出的数据。
- SS,Slave Select,从机选择,也叫做片选信号。一条 SPI 总线可以连接多个从设备,SCLK、MISO 和 MOSI 是共用的,每个从机需要一个独立的片选信号,当从机的 SS 信号拉低时,表示从机被选中,才开始接收总线上的信号。
在一个SPI时钟周期内,收发是同时进行的:
- 主机通过 MOSI 线发送 1bit 数据,从机通过该线读取这 1bit 数据;
- 从机通过 MISO 线发送 1bit 数据,主机通过该线读取这 1bit 数据。
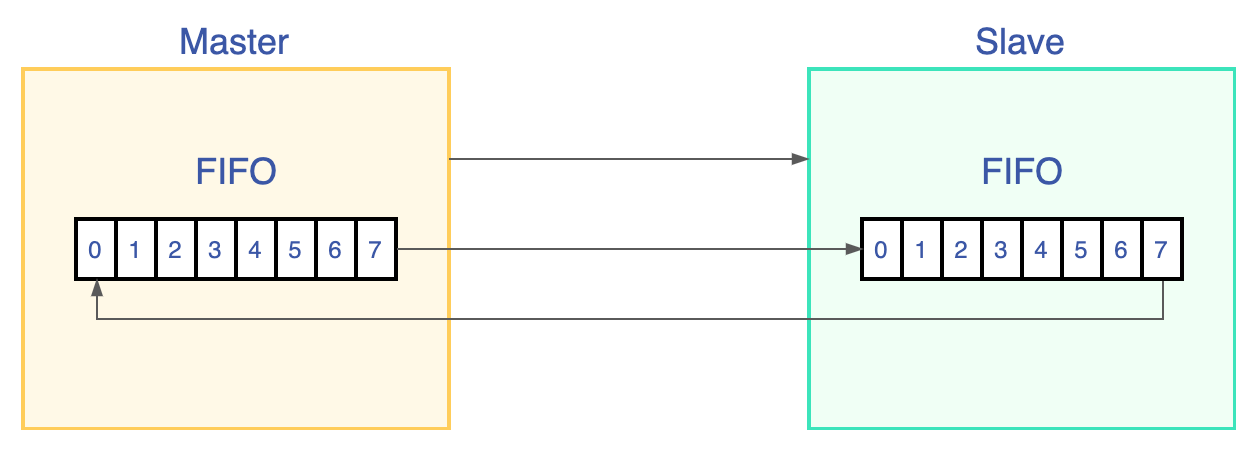
这个过程是 SPI 设备内的移位寄存器实现的,当寄存器中的内容全部移出时,相当于完成了两个寄存器内容的交换,如下图所示。
下面是一个典型的主机模型的通信时序,描述了主机的 0xD2 的数据被移出,从 MISO 信号移入了 0x66 :
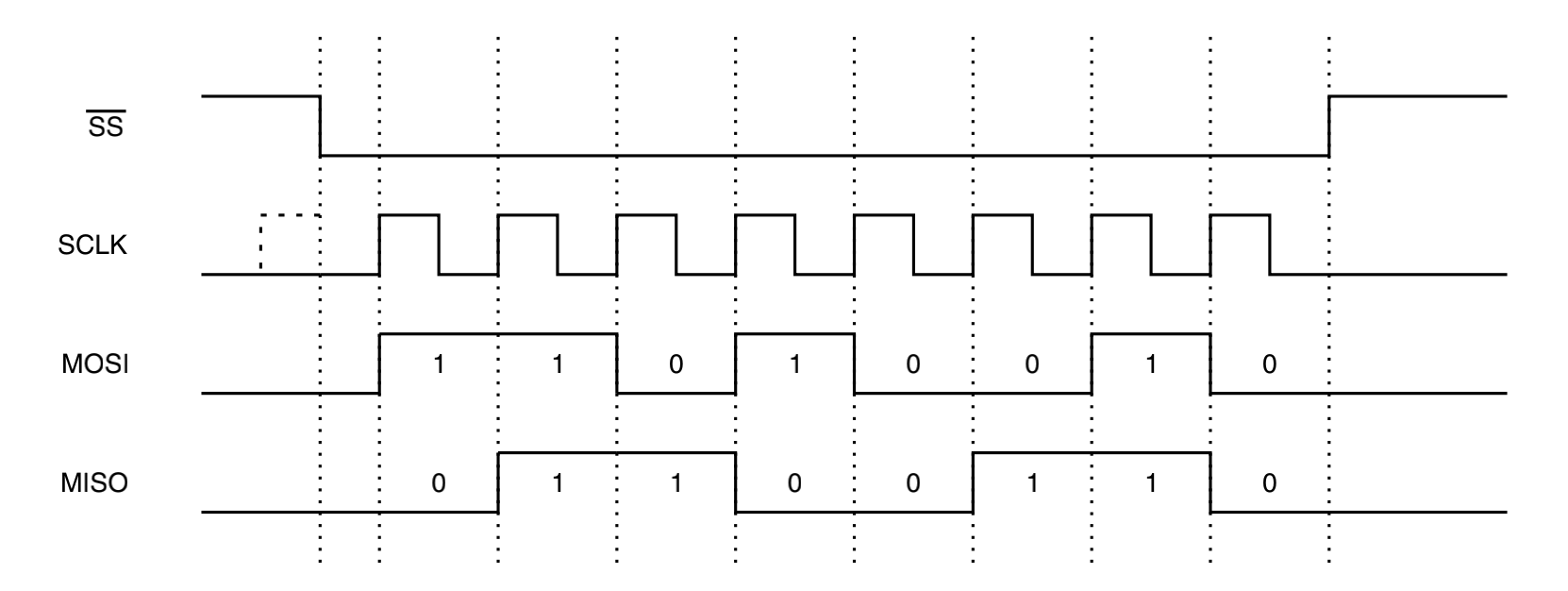
SCLK 、MOSI 和 SS 信号由主机产生,MISO 是从机发出的信号,主机从这个信号读取从机的数据。通信开始前,SCLK 为低电平,当 SS 拉低后,从机被选中,通信开始,MOSI 和 MISO 信号在 SCLK 的上升沿发生变化,MISO 信号在 SCLK 的下降沿被采样锁存,通信结束后,SS 信号拉高,SCLK 信号重回低电平,一次通信发出的 bit 数为一个 word ,也叫字长。这只是一种情况,在 SCLK 下降沿和上升沿所做的事情由 CPOL 和 CPHA 的值决定,可以在 SPI 设备内的寄存器配置:
- CPOL,时钟极性,是指 SS 处于高电平,通信空闲时,SCLK 的电平。CPOL=0 时, SCLK 在空闲状态时为低电平,CPOL=1 时,则相反。
- CPHA,时钟相位,是指通信过程中,数据被采样锁存的时刻。当 CPHA=0 时,MOSI 或 MISO 信号会在 SCLK 的“奇数边沿”被采样,当 CPHA=1 时,信号在 SCLK 的“偶数边沿”采样。
两个配置选项,就会组成四种模式,时序如下图所示:
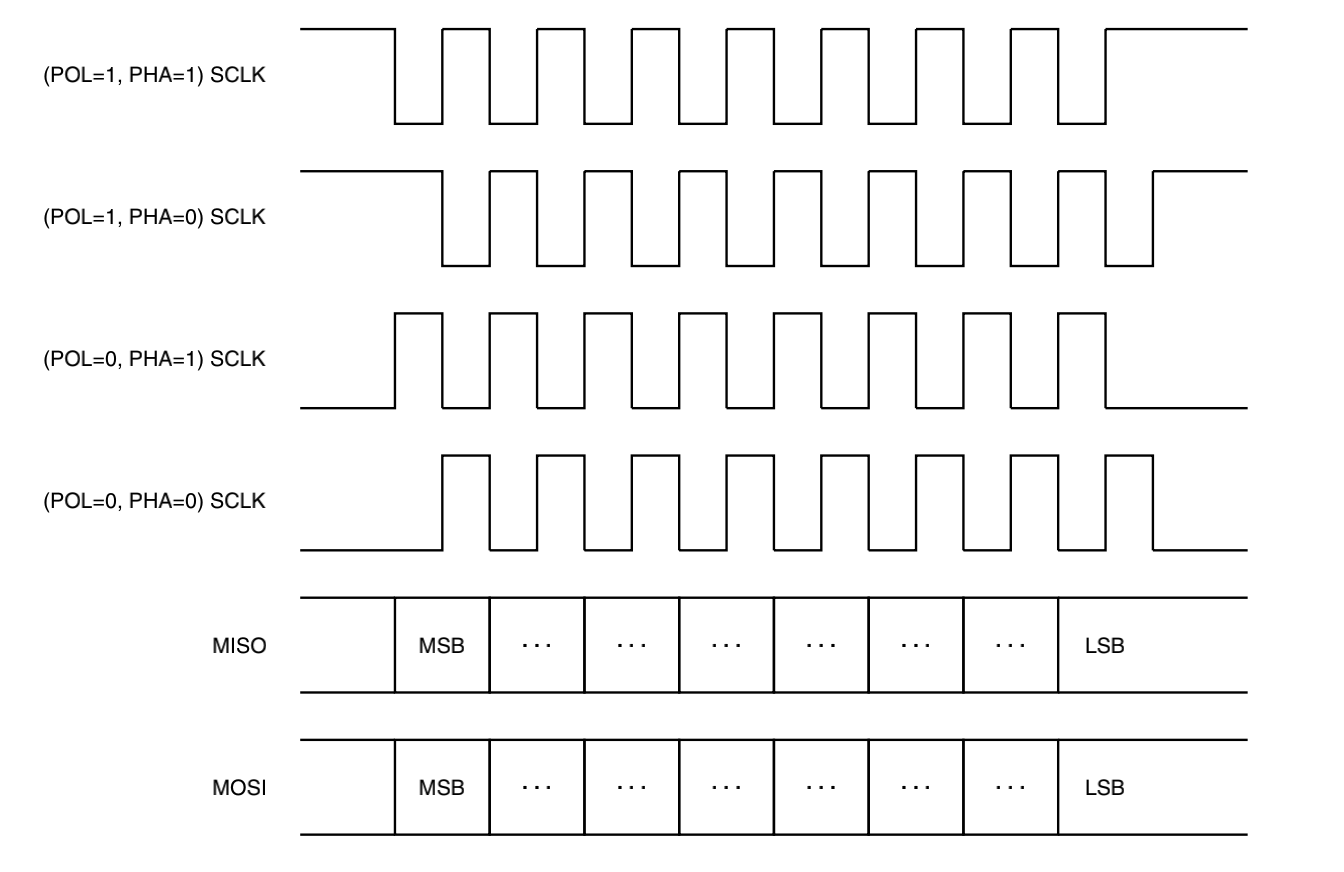
我们需要注意的是,主机和从机必须在相同的模式下才能正常通信。
SPI userspace api #
Linux 的 SPI 驱动生成的 spi 设备文件格式 /dev/spidevB.C ,并提供了功能有限的 API ,可以用 open() 和 close() 函数打开和关闭设备,用 read() 和 write() 函数读写数据,用 ioctl() 发送请求。需要的头文件:
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
首先需要打开设备文件,调用 open() 和 close() 是标准操作,没有特殊之处,例如 open("/dev/spidev0.0", O_RDWR) 。然后调用 ioctl() 进行设置,常用的请求有:
- SPI_IOC_RD_MODE 和 SPI_IOC_WR_MODE 。用于查询(RD)和设置(WR)单字节 SPI 通信的工作模式,包括时钟极性和时钟相位等特性,需要传递一个字符指针,每个位表示一种特性,可用的宏定义在内核源码的
include/uapi/linux/spi/spi.h文件中,常用的有:SPI_MODE_0, 表示 CPOL=0,CPHA=0 。SPI_MODE_1, 表示 CPOL=0,CPHA=1 。SPI_MODE_2, 表示 CPOL=1,CPHA=0 。SPI_MODE_3, 表示 CPOL=1,CPHA=1 。SPI_CS_HIGH, 表示片选信号高电平有效。SPI_LSB_FIRST, 表示按照 LSB 发送,默认是 MSB 发送。
- SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32 和 SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32 。用于查询(RD)和设置(WR)完整的 SPI 通信的工作模式,不再局限于单字节传输。需要传递一个
uint32指针,可用的选项与SPI_IOC_WR_MODE相同。 - SPI_IOC_RD_LSB_FIRST 和 SPI_IOC_WR_LSB_FIRST 。用于查询(RD)和设置(WR)SPI 的发送顺序,需要传递一个字符指针,0 表示 MSB ,其他值表示 LSB 。
- SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD 和 SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD 。用于查询(RD)和设置(WR)SPI 通信的字长,即一次通信发送的 bit 数,需要传递一个字符指针, 0 表示 8bits 。
- SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ 和 SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ 。用于查询(RD)和设置(WR)SPI 的最大传输速率(比特率),单位是 Hz,需要传递一个
uint32型的指针。
配置完毕后就是可以读写,标准的 read() 和 write() 函数显然只能实现半双工,在这些函数调用之间,片选会被停用,要实现全双工需要调用 ioctl() 函数的 SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(n) 请求,n 用于指定传输的次数,读写的数据需要用 struct spi_ioc_transfer 型的指针传递:
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
struct spi_ioc_transfer {
__u64 tx_buf; // 发送缓冲区的指针,里面的数据会发出去,如果为空,会发出 0
__u64 rx_buf; // 接收缓冲区的指针,接收的数据会放在这里,可以为空
__u32 len; // 一次传输的数据长度,单位是字节
__u32 speed_hz; // 临时改变 SPI 的速率
__u16 delay_usecs; // 如果非零,表示两次传输直接的间隔,单位是微秒
__u8 bits_per_word; // 临时改变字长
__u8 cs_change; // 如果非零,下次传输前会取消片选
__u8 tx_nbits;
__u8 rx_nbits;
__u8 word_delay_usecs;
__u8 pad;
}
下面是一个例程,它的作用是向指定的 SPI 设备发送数据,并读回从设备发来的数据。
/*
Copyright (C), SBS Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
Author: LiShaocheng
*/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#define BUF_MAX_SIZE 0x100
static unsigned char mode;
static unsigned char bits_per_word = 8;
static unsigned int speed = 100000;
char *buffer;
void help_info(const char *appname)
{
printf("\n"
"*******************************************************\n"
"*********** Read/Write SPI device test **********\n"
"*******************************************************\n"
"* *\n"
" Options : %s \n"
" [-D spi_dev] [-s speed] \n"
" [-b bits_per_word] \n"
" [-H] [-O] [-C] <value> \n"
"* *\n"
"* <spi_dev> - SPI device name , /dev/spidev0.0 *\n"
"* <speed> - Max transfer speed,Hz *\n"
"* <bits_per_word> - bits per word *\n"
"* -H - Phase 1 operation of clock *\n"
"* -O - Active low polarity of clock *\n"
"* -C - Active high for chip select *\n"
"* <value> - Actual values to be sent *\n"
"*******************************************************\n"
"\n", appname);
}
void numToHexStr(unsigned char _hexNum, unsigned char* _hexStr)
{
unsigned char tmp;
if(NULL == _hexStr)
return;
//低4bit
tmp = (_hexNum >> 4) & 0x0f;
if(tmp <= 9)
*_hexStr = tmp+'0';
else
*_hexStr = tmp-0x0a + 'A';
_hexStr++;
//高4bit
tmp = _hexNum & 0x0f;
if(tmp <= 9)
*_hexStr = tmp+'0';
else
*_hexStr = tmp-0x0a + 'A';
}
//将字符串转为16进制形式,以查看不可见字符 "01" ==> "3031"
int toHexStr(const unsigned char * _str, unsigned char *_hexStr)
{
int i;
int len;
unsigned char* resultPtr;
if(NULL == _str || NULL == _hexStr)
return -1;
len = strlen(_str);
resultPtr = _hexStr;
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
numToHexStr(_str[i], resultPtr);
resultPtr += 2;
}
return strlen(_hexStr);
}
//判断是否是十六进制的基数
int isHexNum(unsigned char _hexNum)
{
if('0'<=_hexNum && _hexNum<='9')
return 1;
else if('A'<=_hexNum && _hexNum<='F')
return 2;
else if('a'<=_hexNum && _hexNum<='f')
return 3;
return -1;
}
//十六进制的字符转数字
unsigned char charToHexNum(unsigned char hexChar)
{
unsigned char tmp;
if(1>isHexNum(hexChar))
return 0xFF;
if(hexChar<='9')
tmp = hexChar-'0';
else if(hexChar<='F')
tmp = hexChar-'7';
else
tmp = hexChar-'W';
return tmp;
}
static int transfer(int fd, char *tbuf, char *rbuf, int bytes)
{
int ret;
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tbuf,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rbuf,
.len = bytes,
};
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret == 1)
printf("can't send spi message");
return ret;
}
int spidev_data_rw(char *dev, int len, char *buffer)
{
char *rbuf;
int res = 0;
int fd = -1;
int i = 0;
fd = open(dev, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("Error:cannot open device "
"(Maybe not present in your board?)\n");
return -1;
}
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE, &mode);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't set spi mode");
goto exit;
}
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MODE, &mode);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't set spi mode");
goto exit;
}
/*
* bits per word
*/
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits_per_word);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't set bits per word");
goto exit;
}
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits_per_word);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't get bits per word");
goto exit;
}
/*
* max speed hz
*/
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't set max speed hz");
goto exit;
}
res = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (res == -1) {
printf("can't get max speed hz");
goto exit;
}
printf("\n");
printf("spi mode: %d\n", mode);
printf("bits per word: %d\n", bits_per_word);
printf("max speed: %d Hz (%d KHz)\n\n", speed, speed/1000);
rbuf = malloc(len);
memset(rbuf, 0, len);
res = transfer(fd, buffer, rbuf, len);
if (res < 0) {
printf("Failed transferring data: %d\n", errno);
free(rbuf);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
printf("Data recived buffer[%d] = 0x%02x\n", i, rbuf[i]);
}
free(rbuf);
exit:
close(fd);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char *spi_dev;
int bytes, len;
int res;
int i;
unsigned char tmp[4];
if (argc <= 1) {
help_info(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
mode = 0;
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-D")) {
i++;
spi_dev = argv[i];
} else if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-s")) {
i++;
speed = atoi(argv[i]);
} else if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-b")) {
i++;
bits_per_word = atoi(argv[i]);
} else if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-H"))
mode |= SPI_CPHA;
else if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-O"))
mode |= SPI_CPOL;
else if(!strcmp(argv[i], "-C"))
mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
else if((i != (argc - 1))) {
printf("invalid parameter\n");
help_info(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
}
// 获得最后一个参数的长度,单位是 byte ,并将数据全部放入 buffer
bytes = strlen((char *)argv[argc - 1]);
if (bytes < 1) {
printf("invalid parameter for buffer size\n");
help_info(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
buffer = malloc(BUF_MAX_SIZE);
memset(buffer, 0, BUF_MAX_SIZE);
strcpy(buffer, (char *)argv[argc-1]);
// 将字符转换为十六进制数字
for(i=0; i<bytes/2; i++)
{
tmp[0] = charToHexNum(buffer[i*2]);
tmp[0] = tmp[0]<<4;
tmp[1] = charToHexNum(buffer[i*2+1]);
buffer[i] = tmp[0] + tmp[1];
printf("Data send buffer[%d] = 0x%02x\n", i, buffer[i]);
}
len = i;
printf("Data send buffer len = 0x%x\n", len);
res = spidev_data_rw(spi_dev, len, buffer);
free(buffer);
return res;
}